Biopsia de próstata
Es el procedimiento utilizado para la extracción de muestras de tejido prostático cuando se sospecha la presencia de adenocarcinoma.
Una prueba precisa
La biopsia de próstata se realiza bajo sugerencia del urólogo cuando este ha detectado en estudios anteriores un desequilibrio en los niveles de antígeno prostático o irregularidades en el tacto rectal.
Se estima que 1 de cada 6 u 8 hombres es propenso a padecer cáncer de próstata.
Es el tipo de cáncer que más afecta a la población masculina alrededor de los 40 años de edad.
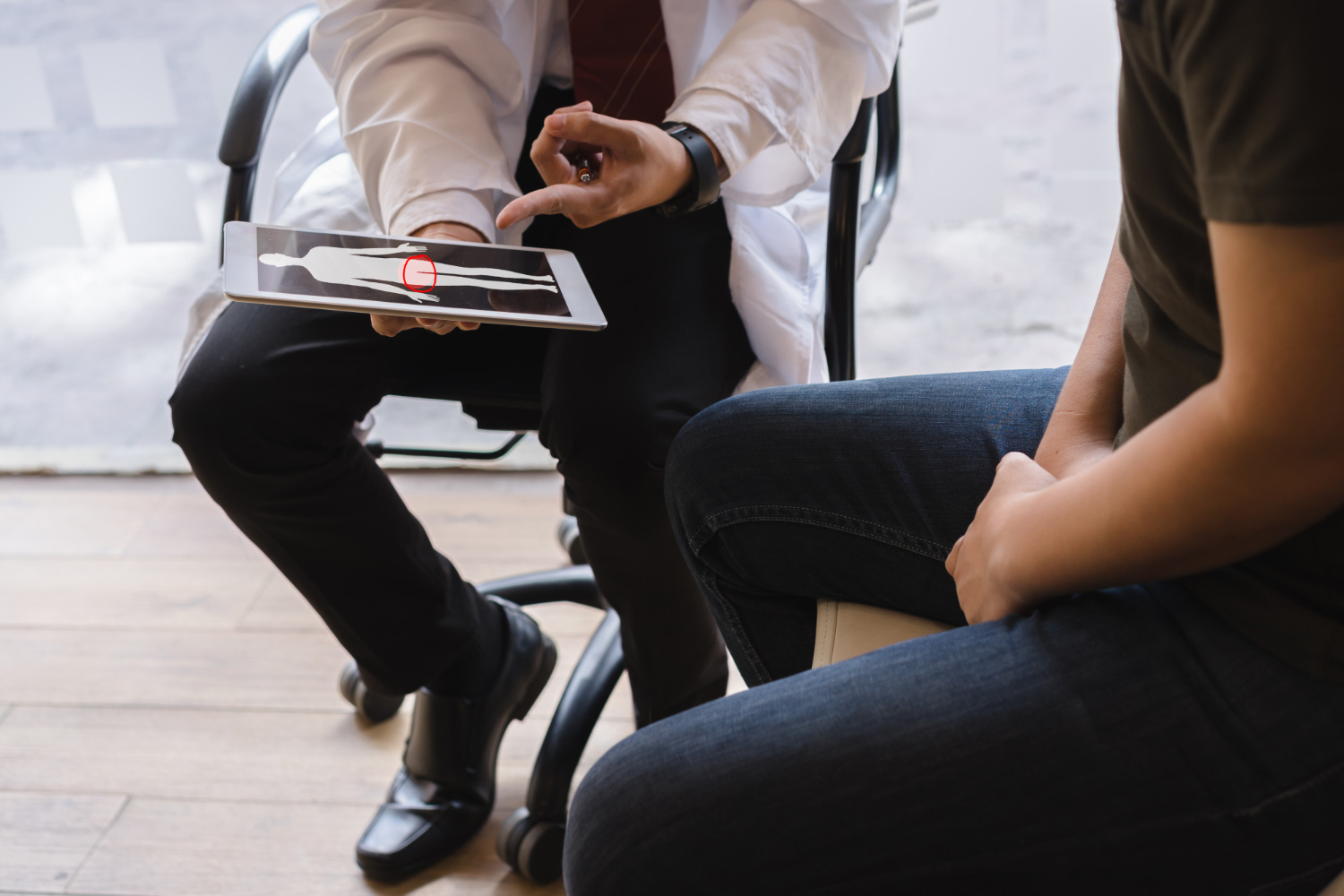


Herramientas tecnológicas
La sonda ecográfica es una de las herramientas a utilizar para obtener imágenes de la próstata y guiar suavemente la aguja hasta el punto exacto de la biopsia.
Insensibilización del área
Al paciente se le aplica una inyección anestésica para ayudar a reducir la sensación de dolor o molestias asociadas al procedimiento.

El Especialista
Nuestros expertos se encargan de realizar este procedimiento de forma profesional empleando todas sus habilidades y experiencias.
El proceso inicia con la limpieza del área y la aplicación de un gel lubricante, seguidamente, el médico urólogo se encargará de introducir una sonda ecográfica dentro del recto para cumplir con 2 funciones esenciales:
- Encontrar el lugar correcto para inyectar la anestesia.
- Orientar la aguja de extracción hasta el punto clave.
Una vez que el médico haya accedido internamente al sitio sospechoso, comenzará a recolectar pequeñas secciones de tejido mediante una delgada aguja accionada por resortes. Estas muestras serán analizadas posteriormente por un patólogo, el cual debe tardar menos de una semana en entregar los resultados del estudio. La biopsia transrectal de próstata ecoguiada suele tardar alrededor de unos 30 minutos en total.
El urólogo puede recomendar una biopsia transrectal de próstata ecoguiada por 4 razones específicas:
- Porque los análisis de antígeno prostático han mostrado niveles más altos que los valores comunes a la edad del paciente.
- Cuando se han encontrado bultos o anomalías durante el tacto rectal de rutina.
- Si los resultados de biopsias anteriores no han sido lo suficientemente concluyentes.
- Si existen hallazgos sospechosos en los estudios de imagen.
Este tipo de procedimiento en ningún momento pone en riesgo la vida del paciente, sin embargo, en ciertos casos se pueden presentar las siguientes afecciones:
- Sangrado rectal luego de la biopsia.
- Presencia de sangre en el semen.
- Aparición de un ligero sangrado en la orina.
- Dificultad temporal para orinar.
- Infección en las vías urinarias o la próstata.
La mayoría de estos síntomas son pasajeros y forman parte de las secuelas normales de este tipo de biopsias, su aparición no debe alarmar al paciente.
Entre las recomendaciones generales se encuentran:
- Poca actividad física dentro de las primeras 24 o 48 horas luego del procedimiento.
- Antibióticos para prevenir infecciones.
- Estar atentos a cualquier tipo de molestías fuertes como: Fiebre alta, dificultad constante para orinar, sangrado o hemorragia intensa, dolor excesivo. Si nota alguno de ellos debe comunicarse de inmediato con su médico.
¿Cómo prepararse antes de una biopsia de próstata?
En las visitas previas al urólogo le indicarán los pasos a seguir para garantizar un diagnóstico exitoso. En la mayoría de los casos, se recomienda detener la toma de medicamentos que puedan retrasar la coagulación como mínimo 1 semana antes de la biopsia de próstata.
El día anterior a la prueba, se aconseja la ingesta de comidas suaves o líquidas; así como también, la aplicación de un enema rectal que le ayude a limpiar completamente sus intestinos. No olvide vestir ropa cómoda y dejar los accesorios y cualquier objeto metálico en casa antes de acudir a esta importante cita médica.
Biopsia de próstata guiada por resonancia magnética (RMN)
Las imágenes por resonancia magnética son un medio muy útil para guiar con precisión las agujas de la biopsia hacia los puntos de la próstata que se quieran estudiar.
También, se utilizan para determinar el estadio y alcance del cáncer en los pacientes con diagnóstico positivo.
Este procedimiento incluye igualmente la colocación de una sonda rectal, por lo que el paciente recibirá sedación para evitar incomodidades durante la prueba.
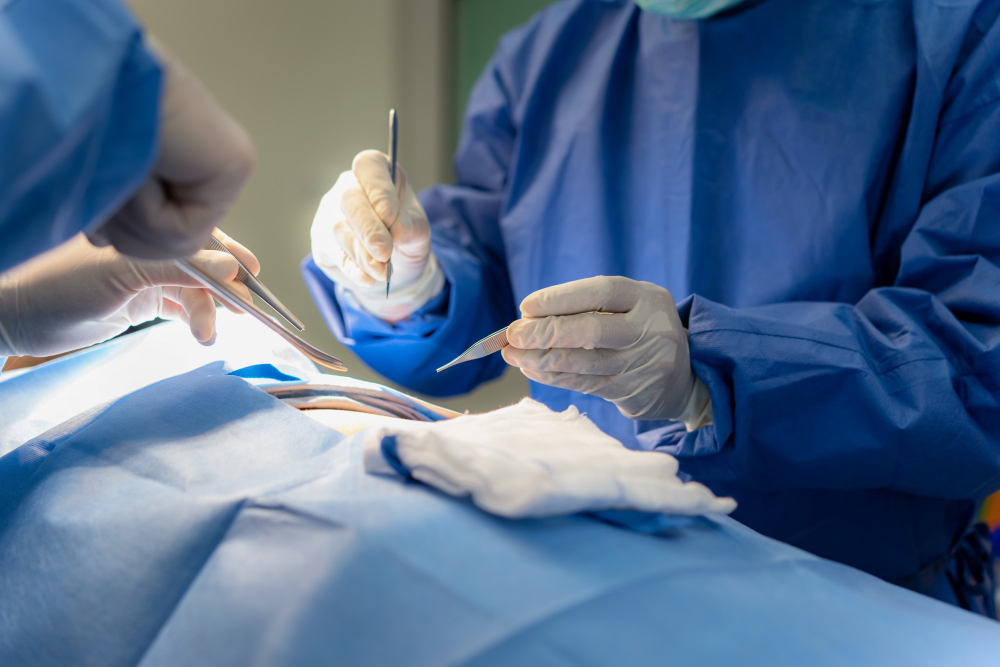
Biopsia transperineal
En este análisis, la vía de abordaje es la extracción de muestras a través de punciones con una aguja fina directamente desde la zona perineal masculina (punto entre el escroto y el recto); de esta manera, se evita la introducción de sondas rectales en aquellos pacientes que cuenten con contraindicaciones al respecto.
Beneficios
- Es la principal prueba diagnóstica para el cáncer de próstata.
- Es una técnica segura y con gran eficacia.
- Como método de prevención permite detectar el cáncer antes de que se propague.
- No es tan invasivo como se cree, las molestías causadas durante la biopsia desaparecen con rapidez.
- Funciona como un medio de vigilancia para corroborar periódicamente el progreso del cáncer en pacientes positivos.
Resultados de la biopsia de próstata
El laboratorio generalmente emite los resultados de una biopsia de próstata en 1 semana o menos. Estos resultados podrían indicar:
- Positivo: Cuando en la muestra se ha observado la presencia de células cancerosas.
- Negativo: Cuando no se ha notado evidencia de cáncer.
- Sospechoso: Cuando la muestra refleja una anomalía, pero esta no es 100% concluyente. Para aclarar las dudas, el especialista podría recomendar una nueva biopsia de próstata en los días siguientes.

Preguntas frecuentes
En la mayoría de los casos suele aplicarse anestesia local para insensibilizar la zona a tratar; por lo que el procedimiento será totalmente indoloro y sólo sentirá el breve pinchazo de la anestesia minutos antes de iniciar la recolección de las muestras.
La toma de una biopsia de próstata no limita la erección ni la sensibilidad del pene. Sin embargo, se recomienda pausar la actividad sexual al menos durante las primeras 48 horas luego del procedimiento
El paciente requerirá la ayuda de un familiar o amigo para trasladarse desde la clínica hasta su casa como cuidado preventivo a los efectos de la anestesia. El médico le podría aconsejar que se mantenga alejado de las actividades físicas vigorosas por los 3 días siguientes a la biopsia; después de unas 48 o 72 horas de reposo relativo, puede retomar sus rutinas progresivamente siempre que no exista dolor.
Durante las primeras 24 o 48 horas el paciente podría experimentar lo siguiente:
- Molestias o sensación de dolor en la zona pélvica.
- Ardor al orinar.
- Micción frecuente.
- Aparición de sangre en la orina o el semen.
- Sangrado rectal.
Generalmente, la toma de medicamentos analgésicos, antibióticos y el descanso por un par de días son suficientes para mejorar todos los síntomas.
Por otra parte, las complicaciones más graves derivadas de una biopsia de próstata incluyen: retención de orina e infección urinaria. Ambas deben ser evaluadas por el médico de forma inmediata.